-
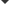
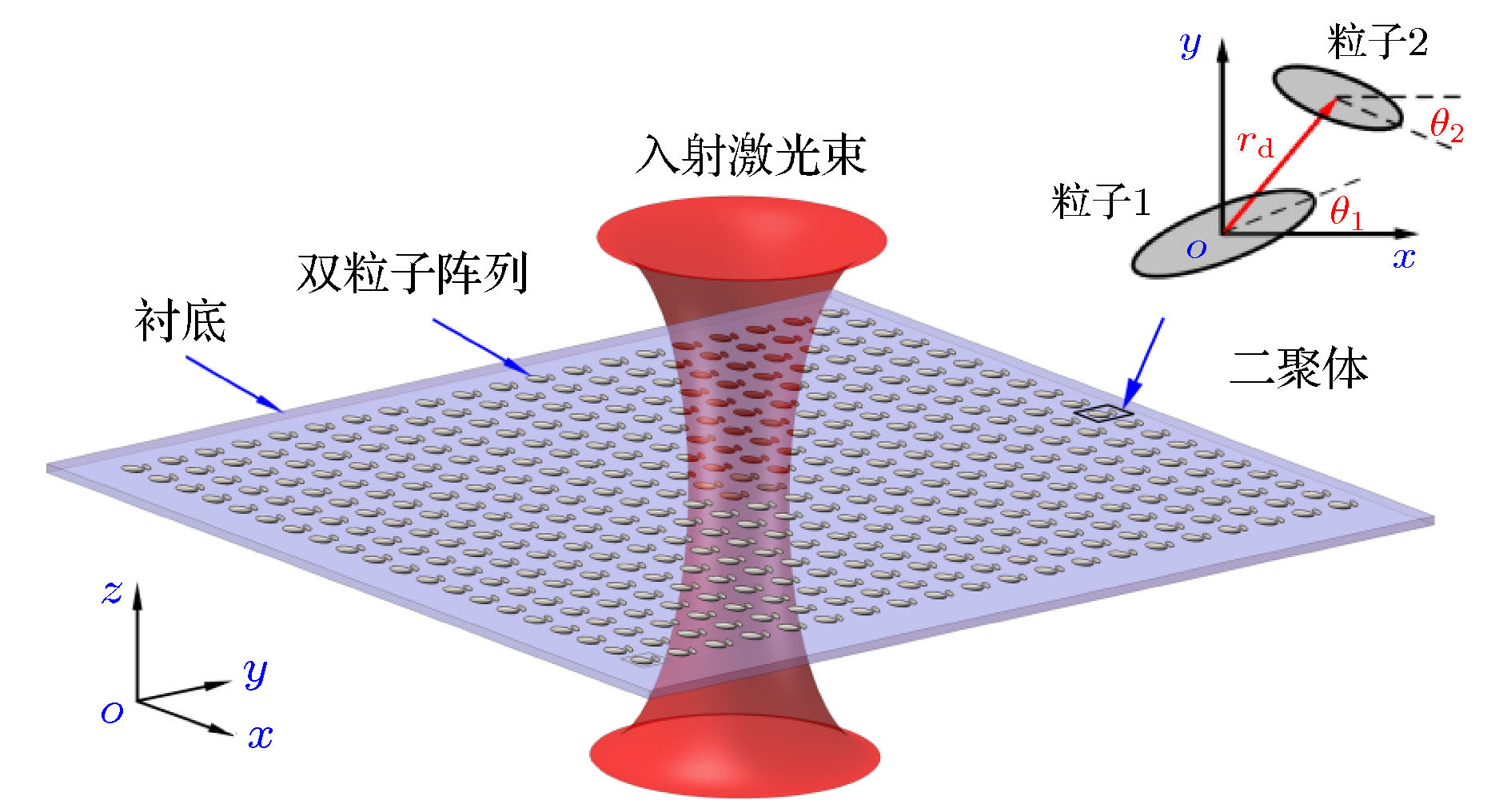
Surface lattice resonance (SLR) relies on both the lattice structure and its unit cell, which usually contains metallic nanoparticles. Since the full width half maximum of the lattice resonance is much narrower than that of localized surface plasmon resonance of a single particle, it is receiving attention increasingly. Based on the modified long-wavelength approximation, in this paper we derive an analytical expression for the extinction cross section of the dimer array of metallic nanoparticles. Comparing with the single particle array, good tunability can be achieved by the lattice resonance of the dimer array, which is influenced by more factors, including the arrangement of the array, the structural parameter and the rotation of the dimer, the shape and size of the particles, etc. First, the polarizabilities of the two kinds of particles in the dimer array are adjusted by introducing a matrix of the array factors, which take into account the influence of dipole fields of every particle. Then a simple expression of the resonance condition for the SLR of the dimmer array is obtained. The proposed model can be applied to a wide variety of dimer arrays of ellipsoid particles, and the applied method can be generalized to more complicated structure like polymer arrays. In this paper we further discuss the polarization dependence and ability to modulate the lattice resonance, by changing the excitation condition and the structural parameters of the dimer array. It is found that the resonances of the dimmer array can be classified as three main categories. The resonance related to the particles is independent of the variation of the dimmer arrangement or the array structure. On the other hand, the resonances corresponding to the dimmer and the array rely crucially on the structural parameters. By carefully adjusting the structural parameters, we can modulate the specific resonance effectively. This research is of theoretical importance for studying the SLR for more complicated structures and may find potential applications in the design of new photoelectric chip via nanoparticle array. -
Keywords:
- scattering /
- surface plasmon /
- dimer
[1] Väkeväinen A I, Moerland R J, Rekola H T, Eskelinen A P, Martikainen J P, Kim D H, Törmä P 2014 Nano Lett. 14 1721
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zhang W, Wu W, Chen S, Zhang J, Ling X, Shu W, Luo H, Wen S 2018 Photonics Res. 6 511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Michaeli L, Keren-Zur S, Avayu O, Suchowski H, Ellenbogen T 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 118 243904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Sun M, Zhang Z, Wang P, Li Q, Ma F, Xu H 2013 Light Sci. Appl. 2 e112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Mi X, Wang Y, Li R, Sun M, Zhang Z, Zheng H 2019 Nanophotonics 8 487
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Kravets V G, Schedin F, Grigorenko A N 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 087403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhou W, Odom T W 2011 Nat. Nanotechnol. 6 423
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Tsoi S, Bezares F J, Giles A, Long J P, Glembocki O J, Caldwell J D, Owrutsky J 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 108 111101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wei A, Kim B, Sadtler B, Tripp S L 2001 ChemPhysChem 2 743
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Hu J, Wang D, Bhowmik D, Liu T, Deng S, Knudson M P, Ao X, Odom T W 2019 ACS Nano 13 4613
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Lin L, Zheng Y 2015 Nanoscale 7 12205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Rechberger W, Hohenau A, Leitner A, Krenn J R, Lamprecht B, Aussenegg F R 2003 Opt. Commun. 220 137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Engheta N, Salandrino A, Alù A 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 95 095504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 周强, 林树培, 张朴, 陈学文 2019 物理学报 68 147104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou Q, Lin S, Zhang P, Chen X 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 147104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 朱旭鹏, 石惠民, 张轼, 陈智全, 郑梦洁, 王雅思, 薛书文, 张军, 段辉高 2019 物理学报 68 147304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu X, Shi H, Zhang S, Chen Z, Zheng M, Wang Y, Xue S, Zhang J, Duan H 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 147304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Alexander M 2009 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 26 517
[17] Hulst H C 1981 Light Scattering by Small Particles (New York: Dover Publications, Inc.) p4
[18] 殷澄, 许田, 陈秉岩, 韩庆邦 2015 物理学报 64 164202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yin C, Xu T, Chen B Y, Han Q B 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 164202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bohren C F, Huffman D R 2008 Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles (Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons) p82
[20] Cai W, Shalaev V 2010 Optical Metamaterials (New York: Springer) p19
-
图 2 在不同偏振光激发下, 单粒子阵列与二聚体阵列的透过率对比 (a)两种阵列模型示意图; (b)二聚体阵列在偏振角度分别为30°, 60°和120°的情况下的透过率; (c), (d)单粒子阵列和二聚体阵列的透过率
Fig. 2. Comparison of the transmission of two different structures under illumination with different polarization: (a) The diagrams of the two arrays; (b) the transmission spectrum of the dimer under different polarization
${\theta _{\rm{p}}} = 30^{\circ}, 60^{\circ}, 120^{\circ} $ , respectively; (c), (d) the calculated transmission of the single particle array and the dimer array, respectively.图 3 在水平偏振光激发下, 方形二聚体阵列的透过率模拟图 (a)计算的模型和参数的定义; (b), (c), (d)二聚体结构参数对透过率的调制效果
Fig. 3. The transmission of the square array of the nanoparticle dimers under illumination of x-axis polarized light: (a) The calculated model and the parameters definition; (b), (c), (d) the modulation on the array transmission by adjusting the dimer arrangement.
-
[1] Väkeväinen A I, Moerland R J, Rekola H T, Eskelinen A P, Martikainen J P, Kim D H, Törmä P 2014 Nano Lett. 14 1721
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zhang W, Wu W, Chen S, Zhang J, Ling X, Shu W, Luo H, Wen S 2018 Photonics Res. 6 511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Michaeli L, Keren-Zur S, Avayu O, Suchowski H, Ellenbogen T 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 118 243904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Sun M, Zhang Z, Wang P, Li Q, Ma F, Xu H 2013 Light Sci. Appl. 2 e112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Mi X, Wang Y, Li R, Sun M, Zhang Z, Zheng H 2019 Nanophotonics 8 487
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Kravets V G, Schedin F, Grigorenko A N 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 087403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhou W, Odom T W 2011 Nat. Nanotechnol. 6 423
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Tsoi S, Bezares F J, Giles A, Long J P, Glembocki O J, Caldwell J D, Owrutsky J 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 108 111101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wei A, Kim B, Sadtler B, Tripp S L 2001 ChemPhysChem 2 743
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Hu J, Wang D, Bhowmik D, Liu T, Deng S, Knudson M P, Ao X, Odom T W 2019 ACS Nano 13 4613
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Lin L, Zheng Y 2015 Nanoscale 7 12205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Rechberger W, Hohenau A, Leitner A, Krenn J R, Lamprecht B, Aussenegg F R 2003 Opt. Commun. 220 137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Engheta N, Salandrino A, Alù A 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 95 095504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 周强, 林树培, 张朴, 陈学文 2019 物理学报 68 147104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou Q, Lin S, Zhang P, Chen X 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 147104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 朱旭鹏, 石惠民, 张轼, 陈智全, 郑梦洁, 王雅思, 薛书文, 张军, 段辉高 2019 物理学报 68 147304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu X, Shi H, Zhang S, Chen Z, Zheng M, Wang Y, Xue S, Zhang J, Duan H 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 147304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Alexander M 2009 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 26 517
[17] Hulst H C 1981 Light Scattering by Small Particles (New York: Dover Publications, Inc.) p4
[18] 殷澄, 许田, 陈秉岩, 韩庆邦 2015 物理学报 64 164202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yin C, Xu T, Chen B Y, Han Q B 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 164202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bohren C F, Huffman D R 2008 Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles (Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons) p82
[20] Cai W, Shalaev V 2010 Optical Metamaterials (New York: Springer) p19
计量
- 文章访问数: 5730
- PDF下载量: 138
- 被引次数: 0












 下载:
下载:



