-
The adsorptions of various gas molecules (H2, H2O, CO, NH3, NO, and NO2) on monolayer GeSe versus the external biaxial strain in a range of –8% to 8% are investigated by first-principles calculations. The band structures, the equilibrium heights, the adsorption energy, and the amount of charge transfer are determined. The calculated results show that monolayer GeSe changes from indirect-to-direct and semiconducting-to-metallic under a certain biaxial strain. The adsorbed gas molecules hardly change the band gap of monolayer GeSe even under a biaxial strain in the whole range from –8% to 8%. The calculated adsorption energies under different strains reveal that the external biaxial strain has no significant effect on the adsorption stability of the gas molecules on monolayer GeSe, so it seems impossible to promote the desorption of the gas molecules by applying strain. It is found that NO2 under the biaxial tensile strain of 8% tends to be bound with the monolayer GeSe by chemical bond which leads to being-difficult-to-desorb. Besides that case, the investigated gas molecules are physisorbed on the GeSe surface and have a certain probability of adsorption and desorption. The charge transfers of CO, NH3, NO and NO2 adsorbed systems under the biaxial strain from –8% to 8% change somehow but are still non-negligible, while for H2 and H2O, their charge transfers are too small to be detected by the monolayer-GeSe-based gas-sensor. Thus, due to the moderate adsorption energy and charge transfer, monolayer GeSe can be a promising candidate as a sensor for CO, NH3 and NO under the biaxial strain from –8% to 8%, and for NO2 in the range from –8% to 6%. It is worth noting that because of the appropriately lower adsorption energy and bigger charge transfer, a bigger biaxial compressive strain, ranging from –6% to –8%, can improve the response speed and sensibility to CO and NO of monolayer GeSe. Furthermore, the effect of the external biaxial strain on the adsorption stability and the charge transfer are discussed based on the two mechanisms of charge transfers, i.e. the traditional and the orbital mixing charge transfer theory. The charge transfer of NH3 is governed by mixing the molecular HOMO with the orbital of GeSe, while for CO, NO and NO2, their charge transfers are most likely determined by different mechanisms under different external strains, which results in different influences on the charge transfer. The present study would be valuable for fully excavating the gas-sensing potential of the two-dimensional GeSe, and then providing sufficient theoretical basis for designing high performance gas sensors based on two-dimensional materials.
-
Keywords:
- gas-sensing /
- strain /
- monolayer-GeSe /
- first-principles
[1] Korotcenkov G 2007 Mater. Sci. Eng. B 139 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zhang R Q, Li B, Yang J L 2015 J. Phys. Chem. C 119 2871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Rastogi P, Kumar S, Bhowmick S, Agarwal A, Chauhant Y S 2014 J. Phys. Chem. C 118 30309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Pu H H, Rhim S H, Gajdardziksa-Josifovska M, Hirschmugl C J, Weinert M, Chen J H 2014 RSC Adv. 4 47481
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhan B B, Li C, Yang J, Jenkins G, Huang W, Dong X C 2014 Small 10 4042
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Schedin F, Geim A K, Morozov S V, Hill E W, Blake P, Katsnelson M I, Novoselov K S 2007 Nat. Mater. 6 652
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Perkins F K, Friedman A L, Cobas E, Campbell P M, Jernigan G G, Jonker B T 2013 Nano Lett. 13 668
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Li H, Yin Z Y, He Q Y, Li H, Huang X, Lu G, Fam D W, Tok A I, Zhang Q, Hua H 2012 Small 8 63
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Yang S X, Yue Q, Cai H, Wu K D, Jiang C B, Tongay S 2016 J. Mater. Chem. C 4 248
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang Y H, Han L F, Xiao Y H, Jia D Z, Guo Z H, Li F 2013 Comp. Mater. Sci. 69 222
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ma L, Zhang J M, Xu K W, Ji V 2015 Appl. Surf. Sci. 343 121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Rad A S, Abedini E 2016 Appl. Surf. Sci. 360 1041
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Luo H, Cao Y J, Zhou J, Feng J M, Cao J M, Guo H 2016 Chem. Phys. Lett. 643 27
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Van Quang V, Van Dung N, SyTrong N, Duc Hoa N, Van Duy N, Van Hieu N 2014 Appl. Phys. Lett. 105 013107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Xia Y, Wang J, Xu J L, Li X, Xie D, Xiang L, Komarneni S 2016 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8 35454
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kim J, Oh S D, Kim J H, Shin D H, Kim S, Choi S -H 2014 Sci. Rep. 4 5384
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Fattah A, Khatami S, Mayorga-Martinez C C, Medina-Sanchez M, Baptista-Pires L, Merkoci A 2014 Small 10 4193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Singh A, Uddin M, Sudarshan T, Koley G 2014 Small 10 1555
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Kim H Y, Lee K, McEvoy N, Yim C, Duesberg G S 2013 Nano Lett. 13 2182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhou C J, Zhu H L, Wu Y P, Lin W, Yang W H, Dong L X 2017 Mater. Chem. Phys. 198 49
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Niu C P, Lan T S, Wang D W, Pan J B, Chu J F, Wang C Y, Yuan H, Yang A J, Wang X H, Rong M Z 2020 Appl. Surf. Sci. 520 146257
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhao H Q, Mao Y L, Mao X, Shi X, Xu C S, Wang C X, Zhang S M, Zhou D H 2018 Adv. Funct. Mater. 28 1704855
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Song X F, Zhou W H, Liu X H, Gu Y, Zhang S L 2017 Phys. B 519 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Hu Y H, Zhang S L, Sun S F, Xie M Q, Cai B, Zeng H B 2015 Appl. Phys. Lett. 107 122107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhou Y, Zhao M, Chen Z W, Shi Z M, Jiang Q 2018 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20 30290
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Brahma M, Kabiraj A, Saha D, Mahapatra S 2018 Sci. Rep. 8 5993
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Guo S Y, Yuan L, Liu X H, Zhou W H, Song X F, Zhang S L 2017 Chem. Phys. Lett. 686 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Liu L, Yang Q, Wang Z P, Ye H Y, Chen X P, Fan X J, Zhang G Q 2018 Appl. Surf. Sci. 433 575
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wang J, Yang G F, Xue J J, Lei J M, Chen D J, Lu H, Zhang R, Zheng Y D 2018 IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 39 599
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Mao Y L, Long L B, Yuan J M, Zhong J X, Zhao H Q 2018 Chem. Phys. Lett. 706 501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Ou J Z, Ge W Y, Carey B, Daeneke T, Rotbart A, Shan W, Wang Y C, Fu Z Q, Chrimes A F, Wiodarski W, Russo S P, Li Y X, Kalantar-zadeh K 2015 ACS Nano 9 10313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Zhou X, Hu X Z, Jin B, Yu J, Liu K L, Li H Q, Zhai T Y 2018 Adv. Sci. 5 1800478
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Hu Z Y, Ding Y C, Hu X M, Zhou W H, Yu X C, Zhang S L 2019 Nanotechnology 30 252001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Wang K, Huang D W, Yu L, Feng K, Li L T, Harada T, Ikeda S, Jiang F 2019 ACS Catal. 9 3090
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Zhuang Q Q, Yang W H, Lin W, Dong L X, Zhou C J 2019 NANO 14 1950131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] 左博敏, 袁健美, 冯志, 毛宇亮 2019 物理学报 68 113103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zuo B M, Yuan J M, Feng Z, Mao Y L 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 113103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Kresse G, Hafner J 1993 Phys. Rev. B 47 558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Kresse G, Furthmüller J 1996 Phys. Rev. B 54 11169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Rochefort A, Wuest D 2009 Langmuir 25 210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Li M M, Zhang J, Li F J, Zhu F X, Zhang M, Zhao X F 2009 Phys. Status Solidi C 6 S90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Blöchl P E 1994 Phys. Rev. B 50 17953
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Monkhorst H J, Pack J D 1976 Phys.Rev. B 13 5188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Henkelman G, Arnaldsson A, Jonsson H 2006 Comput. Mater. Sci. 36 354
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Leenaerts O, Partoens B, Peeters F M 2008 Phys. Rev. B 77 125416
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1 (a) 一个4×4单层GeSe晶胞的俯视和侧视图; (b) 各气体分子在单层GeSe上稳定吸附时的结构示意图, 气体分子从左往右依次为H2, H2O, CO, NH3, NO, NO2; (c) 在单层GeSe的ab平面上施加双轴向应变示意图
Figure 1. (a) Top and side views of the pristine monolayer GeSe; (b) the most favorable configurations for H2, H2O, CO, NH3, NO and NO2 adsorbed on monolayer GeSe, respectively; (c) external biaxial strain applied on monolayer GeSe.
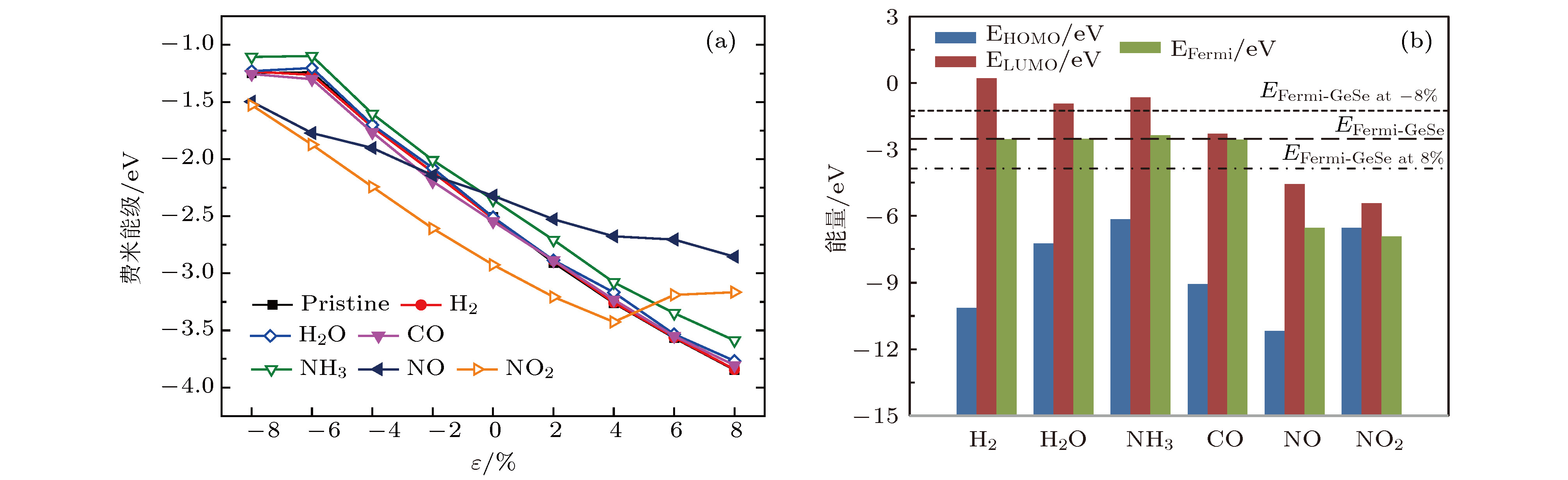
图 4 (a) 各气体分子吸附体系的费米能级与双轴向应变的关系曲线; (b)单层GeSe在–8%—8%双轴向应变范围内的费米能级、气体分子的HOMO和LUMO以及吸附体系的费米能级
Figure 4. (a) Fermi–level of different gas adsorbed systems versus the biaxial strain ranging from –8% to 8%; (b) Fermi-level of pristine monolayer GeSe under the biaxial strain from –8% to 8%, molecular HOMO and LUMO levels and Fermi-levels of the adsorbed systems.
图 5 CO分子吸附体系在双轴向应变 (a) ε = 0和(b) ε = 8%下, NO2分子吸附体系在双轴向应变 (c) ε = 6%和(d) ε = 8%下2.0 × 10–3 e/Å3等能面的差分电荷密度分布图, 其中黄色和蓝色等能面分别表示电子的积聚和耗尽. 图中标出了电荷转移的方向和大小. 插图为单个气体分子的HOMO和LUMO
Figure 5. Side views of the differential charge densities (DCD) for CO adsorbed system at (a) ε = 0 and (b) ε = 8%, NO2 adsorbed system at (a) ε = 6% and (b) ε = 8%, respectively. The isosurface is taken as 2.0 × 10–3 e/Å3. The electron accumulation (depletion) regin on the DCD isosurface is indicated by yellow (blue). The direction (indicated by an arrow) and value of the charge transfer are shown. Insets show the HOMO and LUMO of a single gas molecule.
-
[1] Korotcenkov G 2007 Mater. Sci. Eng. B 139 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zhang R Q, Li B, Yang J L 2015 J. Phys. Chem. C 119 2871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Rastogi P, Kumar S, Bhowmick S, Agarwal A, Chauhant Y S 2014 J. Phys. Chem. C 118 30309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Pu H H, Rhim S H, Gajdardziksa-Josifovska M, Hirschmugl C J, Weinert M, Chen J H 2014 RSC Adv. 4 47481
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhan B B, Li C, Yang J, Jenkins G, Huang W, Dong X C 2014 Small 10 4042
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Schedin F, Geim A K, Morozov S V, Hill E W, Blake P, Katsnelson M I, Novoselov K S 2007 Nat. Mater. 6 652
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Perkins F K, Friedman A L, Cobas E, Campbell P M, Jernigan G G, Jonker B T 2013 Nano Lett. 13 668
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Li H, Yin Z Y, He Q Y, Li H, Huang X, Lu G, Fam D W, Tok A I, Zhang Q, Hua H 2012 Small 8 63
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Yang S X, Yue Q, Cai H, Wu K D, Jiang C B, Tongay S 2016 J. Mater. Chem. C 4 248
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang Y H, Han L F, Xiao Y H, Jia D Z, Guo Z H, Li F 2013 Comp. Mater. Sci. 69 222
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ma L, Zhang J M, Xu K W, Ji V 2015 Appl. Surf. Sci. 343 121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Rad A S, Abedini E 2016 Appl. Surf. Sci. 360 1041
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Luo H, Cao Y J, Zhou J, Feng J M, Cao J M, Guo H 2016 Chem. Phys. Lett. 643 27
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Van Quang V, Van Dung N, SyTrong N, Duc Hoa N, Van Duy N, Van Hieu N 2014 Appl. Phys. Lett. 105 013107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Xia Y, Wang J, Xu J L, Li X, Xie D, Xiang L, Komarneni S 2016 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8 35454
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kim J, Oh S D, Kim J H, Shin D H, Kim S, Choi S -H 2014 Sci. Rep. 4 5384
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Fattah A, Khatami S, Mayorga-Martinez C C, Medina-Sanchez M, Baptista-Pires L, Merkoci A 2014 Small 10 4193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Singh A, Uddin M, Sudarshan T, Koley G 2014 Small 10 1555
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Kim H Y, Lee K, McEvoy N, Yim C, Duesberg G S 2013 Nano Lett. 13 2182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhou C J, Zhu H L, Wu Y P, Lin W, Yang W H, Dong L X 2017 Mater. Chem. Phys. 198 49
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Niu C P, Lan T S, Wang D W, Pan J B, Chu J F, Wang C Y, Yuan H, Yang A J, Wang X H, Rong M Z 2020 Appl. Surf. Sci. 520 146257
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhao H Q, Mao Y L, Mao X, Shi X, Xu C S, Wang C X, Zhang S M, Zhou D H 2018 Adv. Funct. Mater. 28 1704855
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Song X F, Zhou W H, Liu X H, Gu Y, Zhang S L 2017 Phys. B 519 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Hu Y H, Zhang S L, Sun S F, Xie M Q, Cai B, Zeng H B 2015 Appl. Phys. Lett. 107 122107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhou Y, Zhao M, Chen Z W, Shi Z M, Jiang Q 2018 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20 30290
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Brahma M, Kabiraj A, Saha D, Mahapatra S 2018 Sci. Rep. 8 5993
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Guo S Y, Yuan L, Liu X H, Zhou W H, Song X F, Zhang S L 2017 Chem. Phys. Lett. 686 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Liu L, Yang Q, Wang Z P, Ye H Y, Chen X P, Fan X J, Zhang G Q 2018 Appl. Surf. Sci. 433 575
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wang J, Yang G F, Xue J J, Lei J M, Chen D J, Lu H, Zhang R, Zheng Y D 2018 IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 39 599
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Mao Y L, Long L B, Yuan J M, Zhong J X, Zhao H Q 2018 Chem. Phys. Lett. 706 501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Ou J Z, Ge W Y, Carey B, Daeneke T, Rotbart A, Shan W, Wang Y C, Fu Z Q, Chrimes A F, Wiodarski W, Russo S P, Li Y X, Kalantar-zadeh K 2015 ACS Nano 9 10313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Zhou X, Hu X Z, Jin B, Yu J, Liu K L, Li H Q, Zhai T Y 2018 Adv. Sci. 5 1800478
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Hu Z Y, Ding Y C, Hu X M, Zhou W H, Yu X C, Zhang S L 2019 Nanotechnology 30 252001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Wang K, Huang D W, Yu L, Feng K, Li L T, Harada T, Ikeda S, Jiang F 2019 ACS Catal. 9 3090
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Zhuang Q Q, Yang W H, Lin W, Dong L X, Zhou C J 2019 NANO 14 1950131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] 左博敏, 袁健美, 冯志, 毛宇亮 2019 物理学报 68 113103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zuo B M, Yuan J M, Feng Z, Mao Y L 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 113103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Kresse G, Hafner J 1993 Phys. Rev. B 47 558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Kresse G, Furthmüller J 1996 Phys. Rev. B 54 11169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Rochefort A, Wuest D 2009 Langmuir 25 210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Li M M, Zhang J, Li F J, Zhu F X, Zhang M, Zhao X F 2009 Phys. Status Solidi C 6 S90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Blöchl P E 1994 Phys. Rev. B 50 17953
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Monkhorst H J, Pack J D 1976 Phys.Rev. B 13 5188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Henkelman G, Arnaldsson A, Jonsson H 2006 Comput. Mater. Sci. 36 354
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Leenaerts O, Partoens B, Peeters F M 2008 Phys. Rev. B 77 125416
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 4936
- PDF Downloads: 118
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: