-
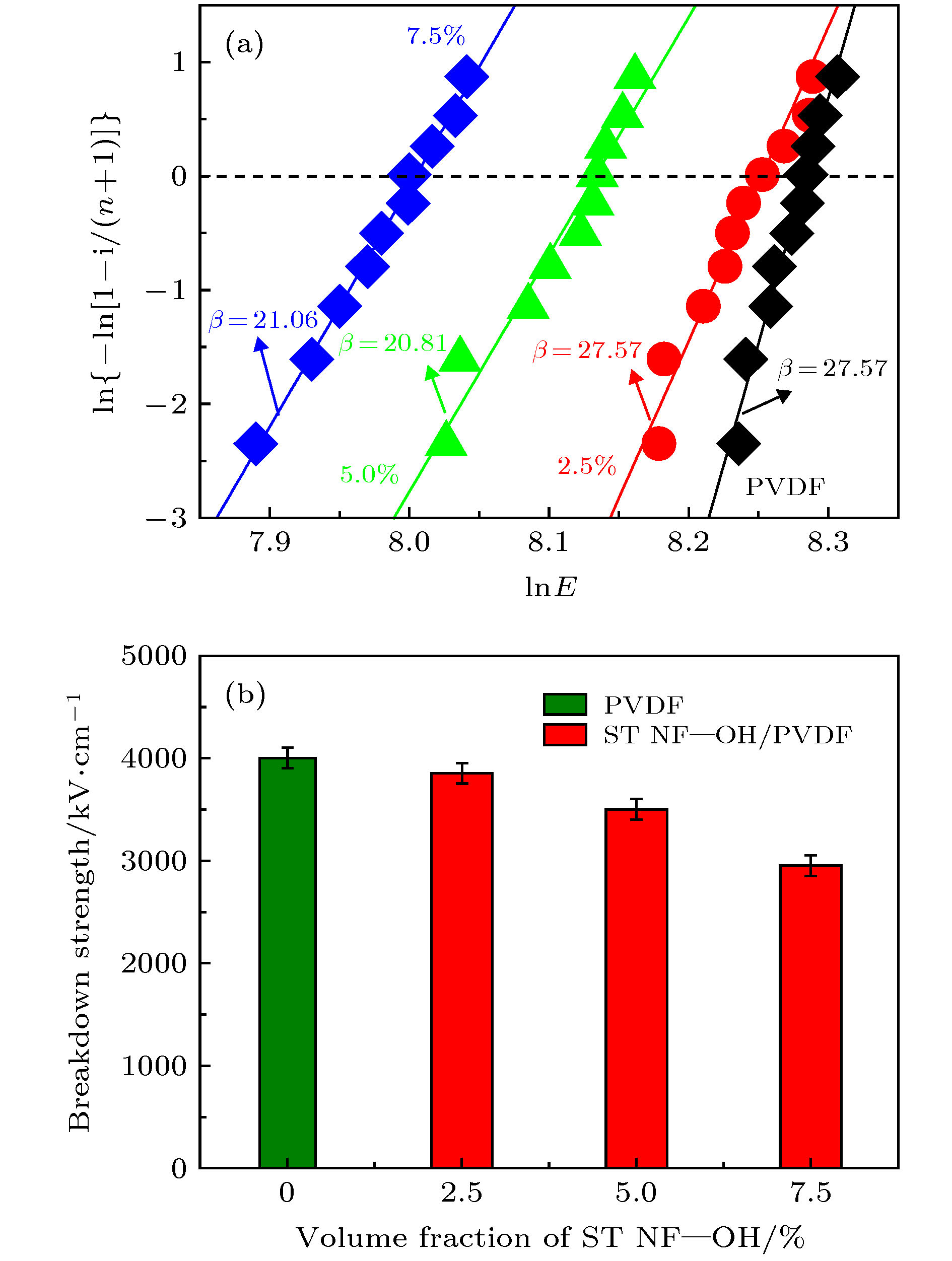
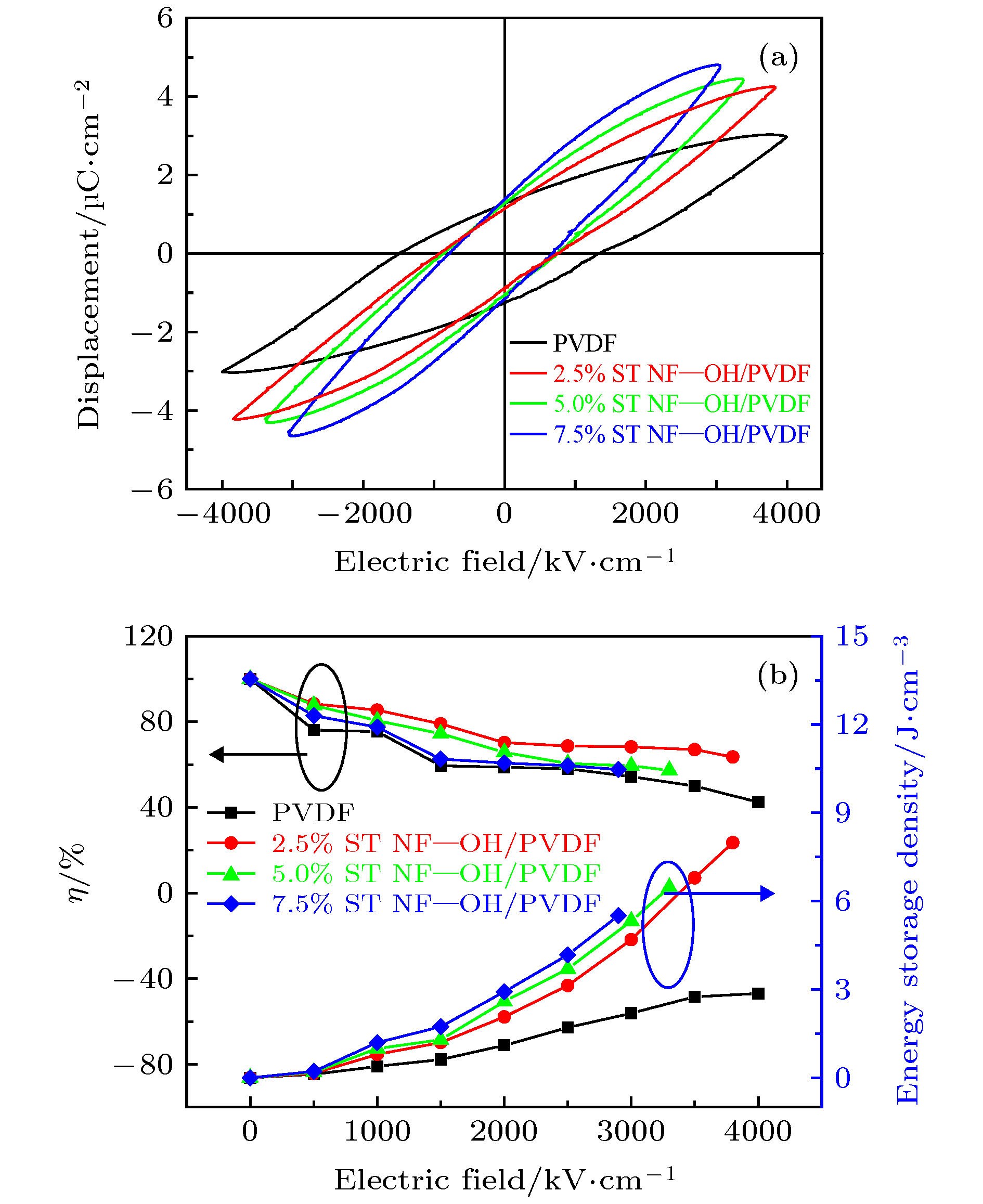
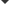
With the rapid development of the electronics industry, the dielectric materials with high energy storage density, fast charge and discharge speed, easy-to-process and easy-to-mold, and stable performance are urgently needed to meet the requirements for lightweight and miniaturization of electronic component equipment. Dielectric ceramics has a high dielectric constant, but low breakdown field strength. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) has the advantages of good flexibility, high breakdown field strength, and light weight, but its dielectric constant is low. Achieving the ability to tailor the interface between dielectric ceramics filler and PVDF polymer matrix is a key issue for realizing the desirable dielectric properties and high energy density in the nanocomposites. As a result, much effort has been made to prepare the polymer composites through the surface modification of the nanoparticles with high dielectric constant fillers dispersed in a matrix, with the hope of preparing composites containing the high dielectric constant of the ceramic fillers and the high breakdown strength of polymers. In this work, in order to obtain the high dielectric-constant and high-energy-storage-density dielectric ceramics, the electrospinning method is used to prepare the SrTiO3 one-dimensional nanofibers as the inorganic fillers and the casting method is adopted to prepare PVDF as the polymer matrix. To improve the interface between inorganic nanofiber fillers and PVDF matrix, the SrTiO3 nanofibers are modified by surface hydroxylation. The effects of suface hydroxylated SrTiO3 nanofibers on the dielectric properties and energy storage properties of PVDF composites are studied. The correlation between interface modification and energy storage performance of composites is investigated to reveal the mechanism of enhanced energy storage performance of SrTiO3 nanofibers/PVDF composites. The results show that the dispersion of surface-hydroxylating SrTiO3 nanofibers in PVDF polymer can be improved. The composites exhibit improved dielectric properties and enhanced breakdown strength. When the filling quantity of the surface-hydroxylating SrTiO3 nanofiber fillers is 2.5 vol%, the energy storage density of the composite reaches 7.96 J/cm3. Suface-hydroxylating SrTiO3 nanofibers exhibit excellent dispersion in the PVDF polymer matrix and strong interfacial adhesion with the matrix, leading the composites to possess excellent dielectric constant and energy storage performance. The surface hydroxylation of ceramic fillers can improve the energy storage performance of the composites.
-
Keywords:
- strontium titanate /
- energy storage property /
- nanofiber /
- surface modification
[1] Wang Y, Wang L, Yuan Q, Niu Y, Chen J, Wang Q, Wang H 2017 J. Mater. Chem. A 5 10849
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Luo H, Roscow J, Zhou X, Chen S, Han X, Zhou K, Zhang D, Bowen C R 2017 J. Mater. Chem. A 5 7091
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhang X, Shen Y, Xu B, Zhang Q H, Gu L, Jiang J Y, Ma J, Lin Y H, Nan C W 2016 Adv. Mater. 28 2055
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhu Y, Zhu Y, Huang X, Chen J, Li Q, He J, Jiang P 2019 Adv. Energy Mater. 9 1901826
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Luo H, Ma C, Zhou X, Chen S, Zhang D 2017 Macromolecules 50 5132
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Shen Z H, Wang J J, Jiang J Y, Lin Y H, Nan C W, Chen L Q, Shen Y 2018 Adv. Energy Mater. 8 1800509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhang D, Zhou X, Roscow J, Zhou K, Wang L, Luo H, Bowen C R 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 45179
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Dang Z M, Yuan J K, Zha J W, Zhou T, Li S T, Hu G H 2012 Prog. Mate.r Sci. 57 660
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhou Y, Li Q, Dang B, Yang Y, Shao T, Li H, Hu J, Zeng R, He J, Wang Q 2018 Adv. Mater. 30 1805672
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Yao Z, Song Z, Hao H, Yu Z, Cao M, Zhang S, Lanagan M T, Liu H 2017 Adv. Mater. 29 1601727
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 赵学童, 廖瑞金, 李建英, 王飞鹏 2015 物理学报 64 127701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao X T, Liao R J, Li J Y, Wang F P 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 127701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 冯奇, 李梦凯, 唐海通, 王晓东, 高忠民, 孟繁玲 2016 物理学报 65 188101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Feng Q, Li M K, Tang H T, Wang X D, Gao Z M, Meng F L 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 188101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Song Y, Shen Y, Liu H Y, Lin Y H, Li M, Nan C W 2012 J. Mate.r Chem. 22 8063
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Song Y, Shen Y, Hu P H, Lin Y H, Li M, Nan C W 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 101 152904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Xie L Y, Huang X Y, Wu C, Jiang P K 2011 J. Mater. Chem. 21 5897
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Xie L Y, Huang X Y, Yang K, Li S T, Jiang P K 2014 J. Mater. Chem. A 2 5244
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Thakur V K, Lin M F, Tan E J, Lee P S 2012 J. Mater. Chem. 22 5951
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Thakur V K, Tan E J, Lin M F, Lee P S 2011 Polym. Chem. 2 2000
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Thakur V K, Yan J, Lin M F, Zhi C Y, Golberg D, Bando Y, Sim R, Lee P S 2012 Polym. Chem. 3 962
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wang X, Dai Y Y, Wang W M, Ren M M, Li B Y, Fan C, Liu X Y 2014 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6 16182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Almadhoun M N, Bhansali U S, Alshareef H N 2012 J. Mater. Chem. 22 11196
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Yuan X P, Matsuyama Y, Chung T C M 2010 Macromolecules 43 4011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhang Q P, Xia W M, Zhu Z G, Zhang Z C 2013 J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 127 3002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Zhang Z C, Chung T C M 2007 Macromolecules 40 9391
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Yu K, Wang H, Zhou Y C, Bai Y Y, Niu Y J 2013 J. Appl. Phys. 113 034105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Wang Z P, Nelson J K, Miao J J, Linhardt R J, Schadler L S, Hillborg H, Zhao S 2012 IEEE Trans. Dielect. El. In. 19 960
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Kim P, Doss N M, Tillotson J P, Hotchkiss P J, Pan M J, Marder S R, Li J Y, Calame J P, Perry J W 2009 ACS Nano 3 2581
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 王璐, 孔文杰, 罗行, 周学凡, 周科朝, 张斗 2018 无机材料学报 33 1060
Wang L, Kong W J, Luo H, Zhou X F, Zhou K C, Zhang D 2018 Journal of Inorganic Materials 33 1060
[29] Xia W M, Xu Z, Wen F, Zhang Z C 2012 Ceram. Int. 38 1071
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 羟基化处理前后样品的晶体结构
Table 1. Crystal structure of the samples before and after hydroxylation.
样品 PDF卡片编号 晶相 空间群 晶格参数/nm ST NF 35-0734 立方相 Pm- 3m a = b = c = 0.3911 ST NF—OH 35-0734 立方相 Pm-3m a = b = c = 0.3915 表 2 前期文献报道的PVDF基复合材料的储能密度与本文实验结果比较
Table 2. Comparison of the energy storage density of PVDF-based composite materials reported in previous literatures and the experimental results in this paper.
-
[1] Wang Y, Wang L, Yuan Q, Niu Y, Chen J, Wang Q, Wang H 2017 J. Mater. Chem. A 5 10849
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Luo H, Roscow J, Zhou X, Chen S, Han X, Zhou K, Zhang D, Bowen C R 2017 J. Mater. Chem. A 5 7091
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhang X, Shen Y, Xu B, Zhang Q H, Gu L, Jiang J Y, Ma J, Lin Y H, Nan C W 2016 Adv. Mater. 28 2055
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhu Y, Zhu Y, Huang X, Chen J, Li Q, He J, Jiang P 2019 Adv. Energy Mater. 9 1901826
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Luo H, Ma C, Zhou X, Chen S, Zhang D 2017 Macromolecules 50 5132
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Shen Z H, Wang J J, Jiang J Y, Lin Y H, Nan C W, Chen L Q, Shen Y 2018 Adv. Energy Mater. 8 1800509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhang D, Zhou X, Roscow J, Zhou K, Wang L, Luo H, Bowen C R 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 45179
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Dang Z M, Yuan J K, Zha J W, Zhou T, Li S T, Hu G H 2012 Prog. Mate.r Sci. 57 660
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhou Y, Li Q, Dang B, Yang Y, Shao T, Li H, Hu J, Zeng R, He J, Wang Q 2018 Adv. Mater. 30 1805672
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Yao Z, Song Z, Hao H, Yu Z, Cao M, Zhang S, Lanagan M T, Liu H 2017 Adv. Mater. 29 1601727
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 赵学童, 廖瑞金, 李建英, 王飞鹏 2015 物理学报 64 127701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao X T, Liao R J, Li J Y, Wang F P 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 127701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 冯奇, 李梦凯, 唐海通, 王晓东, 高忠民, 孟繁玲 2016 物理学报 65 188101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Feng Q, Li M K, Tang H T, Wang X D, Gao Z M, Meng F L 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 188101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Song Y, Shen Y, Liu H Y, Lin Y H, Li M, Nan C W 2012 J. Mate.r Chem. 22 8063
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Song Y, Shen Y, Hu P H, Lin Y H, Li M, Nan C W 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 101 152904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Xie L Y, Huang X Y, Wu C, Jiang P K 2011 J. Mater. Chem. 21 5897
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Xie L Y, Huang X Y, Yang K, Li S T, Jiang P K 2014 J. Mater. Chem. A 2 5244
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Thakur V K, Lin M F, Tan E J, Lee P S 2012 J. Mater. Chem. 22 5951
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Thakur V K, Tan E J, Lin M F, Lee P S 2011 Polym. Chem. 2 2000
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Thakur V K, Yan J, Lin M F, Zhi C Y, Golberg D, Bando Y, Sim R, Lee P S 2012 Polym. Chem. 3 962
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wang X, Dai Y Y, Wang W M, Ren M M, Li B Y, Fan C, Liu X Y 2014 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6 16182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Almadhoun M N, Bhansali U S, Alshareef H N 2012 J. Mater. Chem. 22 11196
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Yuan X P, Matsuyama Y, Chung T C M 2010 Macromolecules 43 4011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhang Q P, Xia W M, Zhu Z G, Zhang Z C 2013 J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 127 3002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Zhang Z C, Chung T C M 2007 Macromolecules 40 9391
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Yu K, Wang H, Zhou Y C, Bai Y Y, Niu Y J 2013 J. Appl. Phys. 113 034105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Wang Z P, Nelson J K, Miao J J, Linhardt R J, Schadler L S, Hillborg H, Zhao S 2012 IEEE Trans. Dielect. El. In. 19 960
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Kim P, Doss N M, Tillotson J P, Hotchkiss P J, Pan M J, Marder S R, Li J Y, Calame J P, Perry J W 2009 ACS Nano 3 2581
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 王璐, 孔文杰, 罗行, 周学凡, 周科朝, 张斗 2018 无机材料学报 33 1060
Wang L, Kong W J, Luo H, Zhou X F, Zhou K C, Zhang D 2018 Journal of Inorganic Materials 33 1060
[29] Xia W M, Xu Z, Wen F, Zhang Z C 2012 Ceram. Int. 38 1071
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 7127
- PDF Downloads: 129
- Cited By: 0













 DownLoad:
DownLoad: