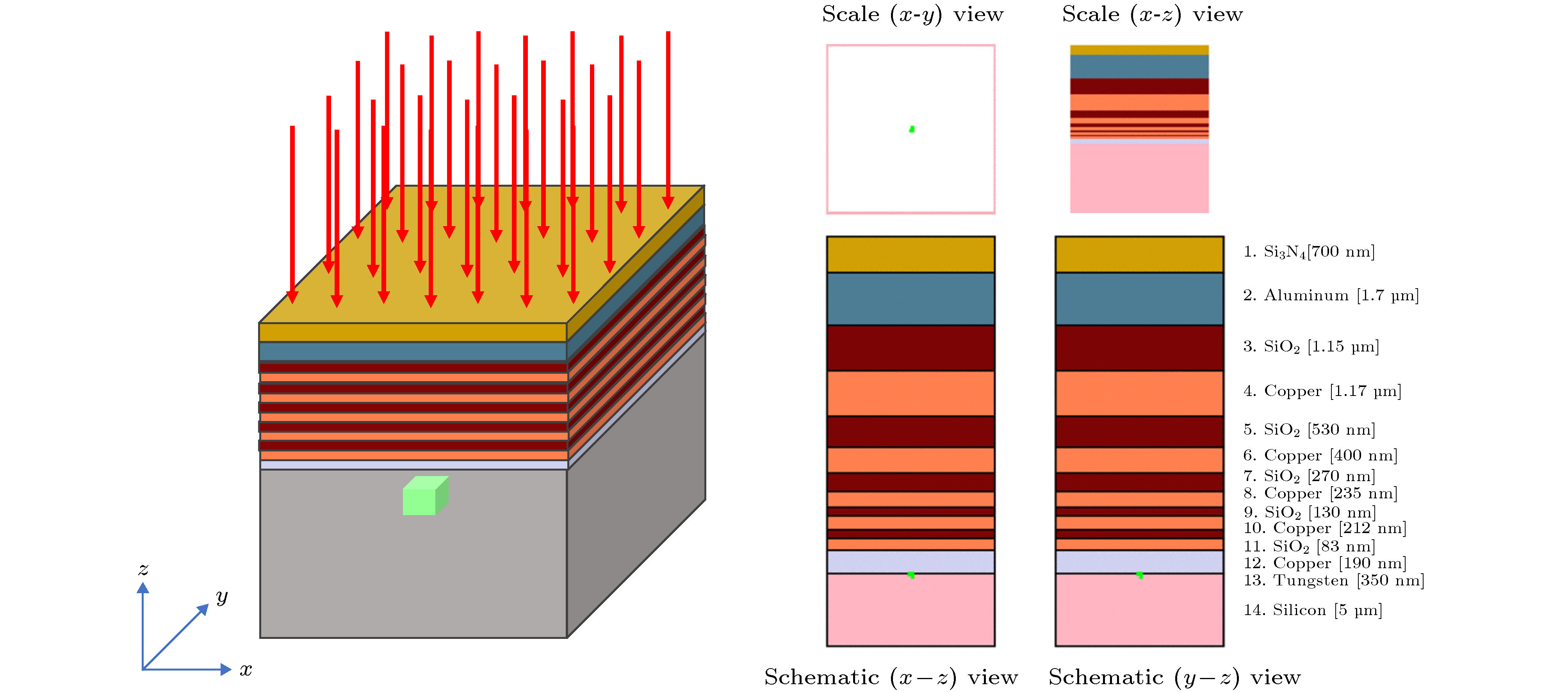
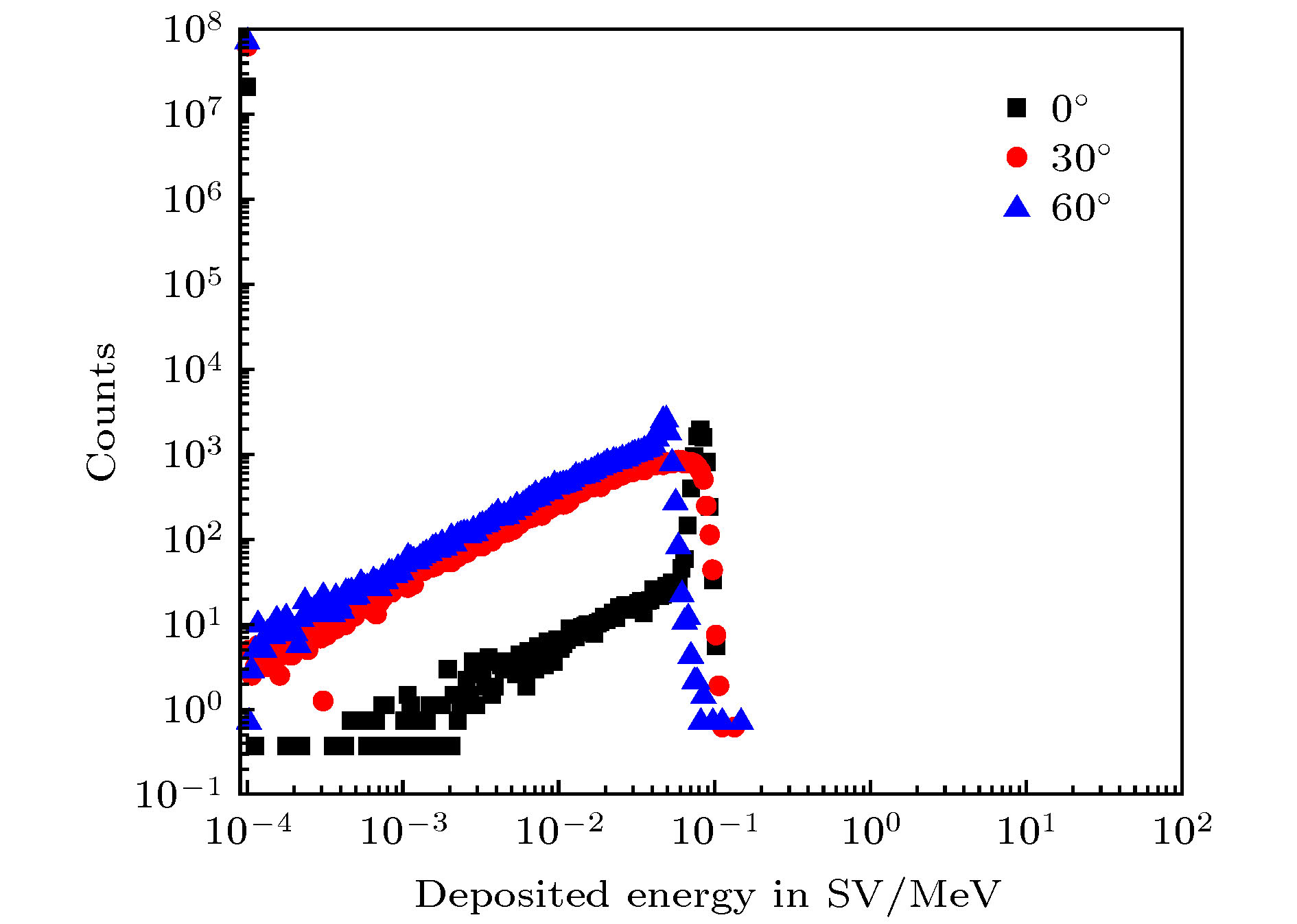
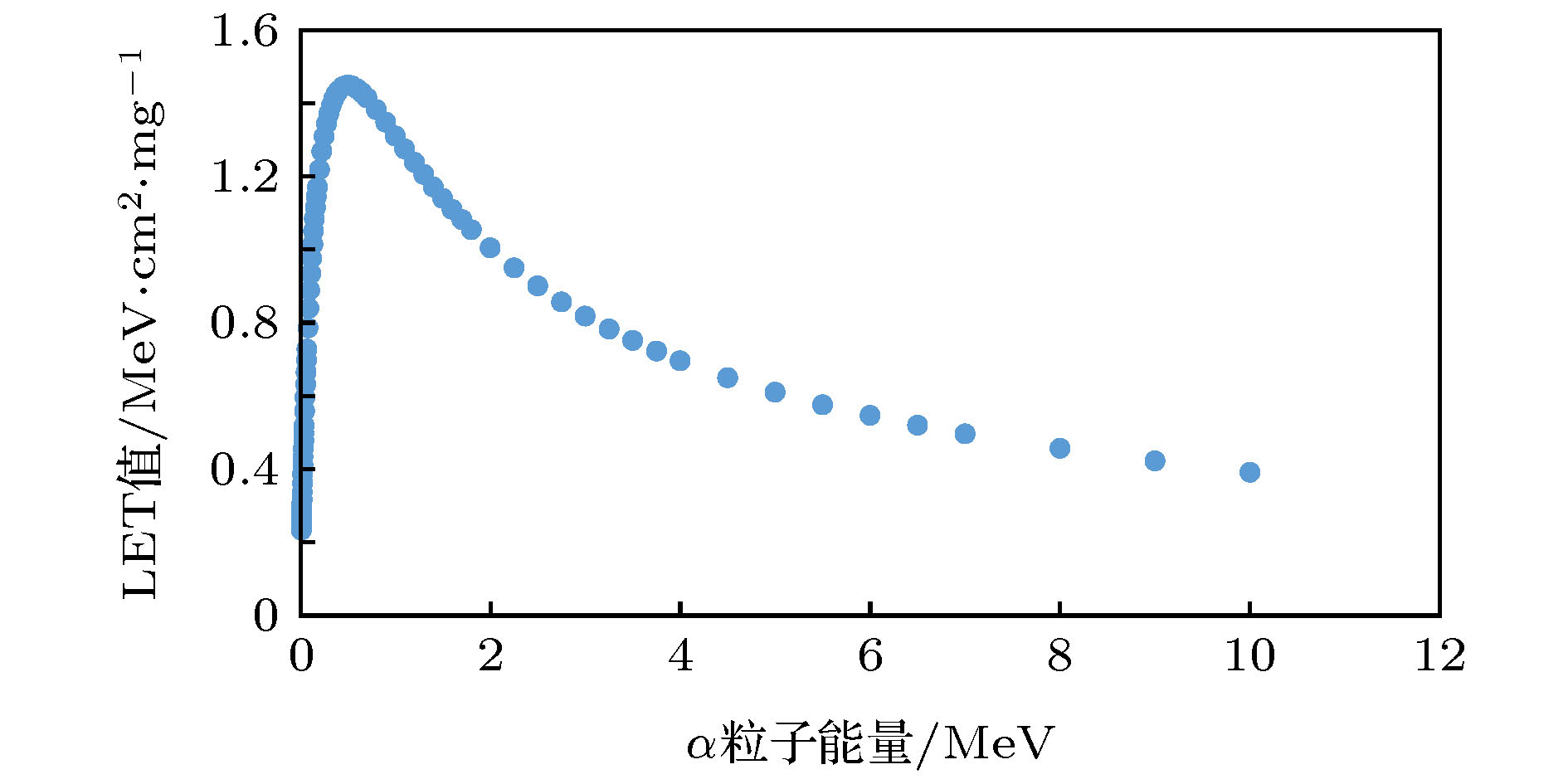
-
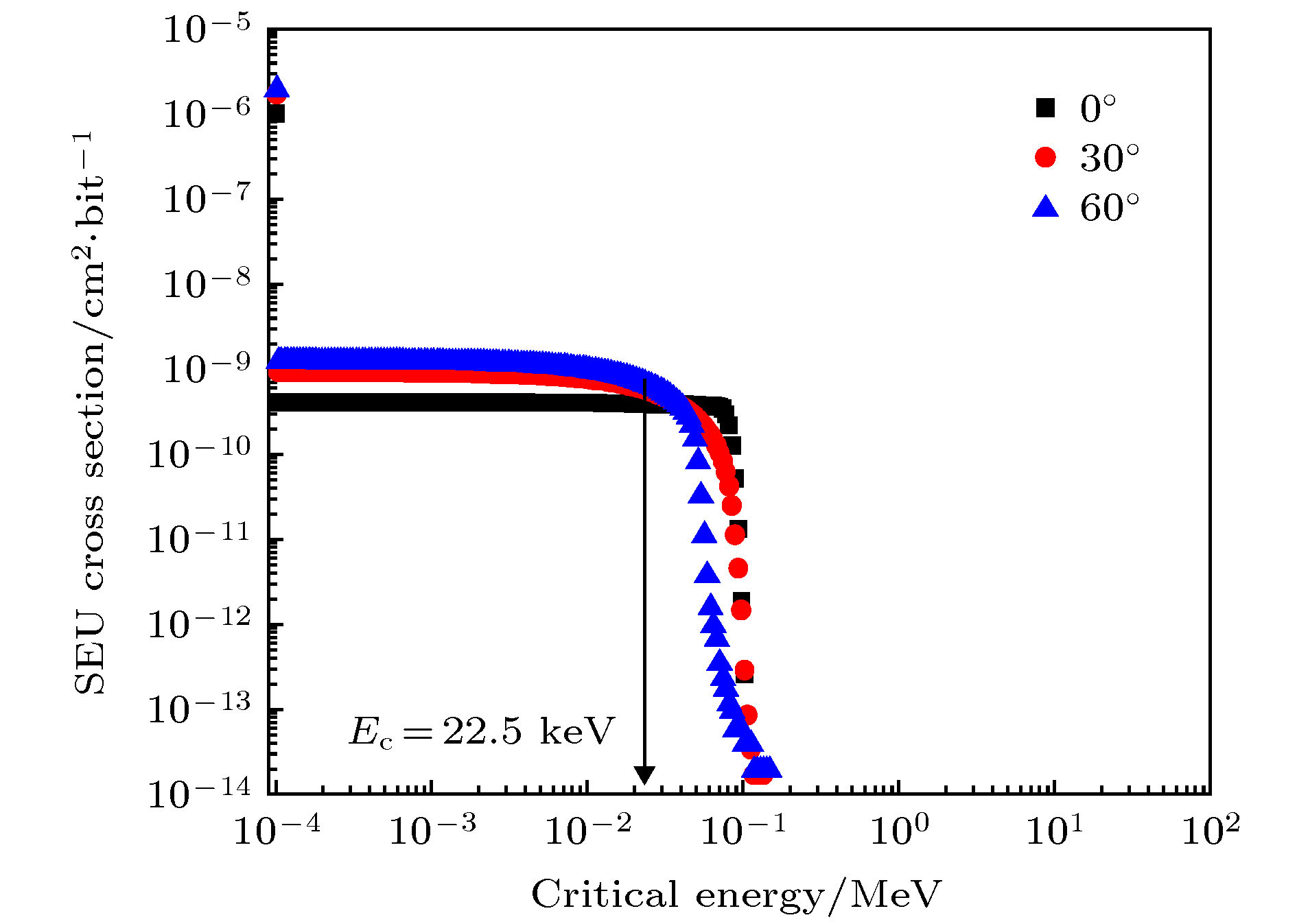
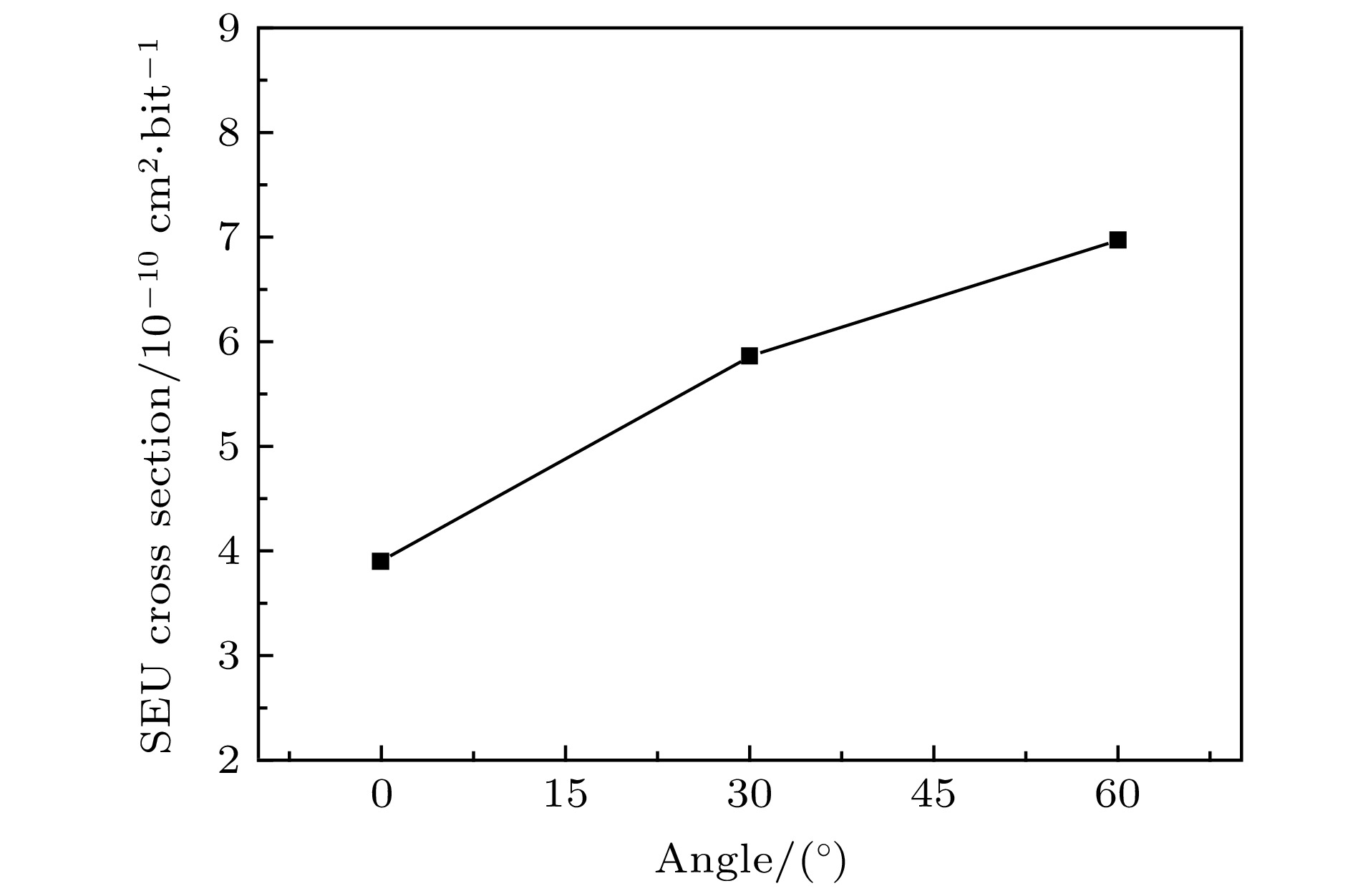
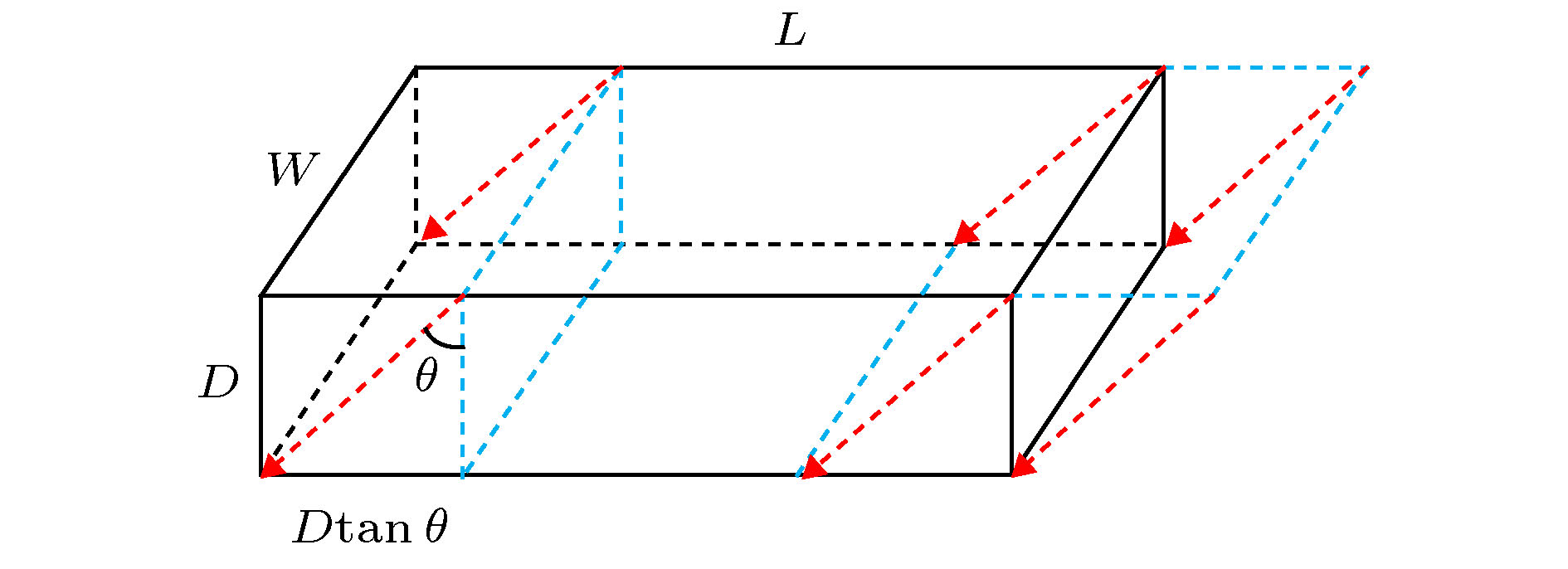
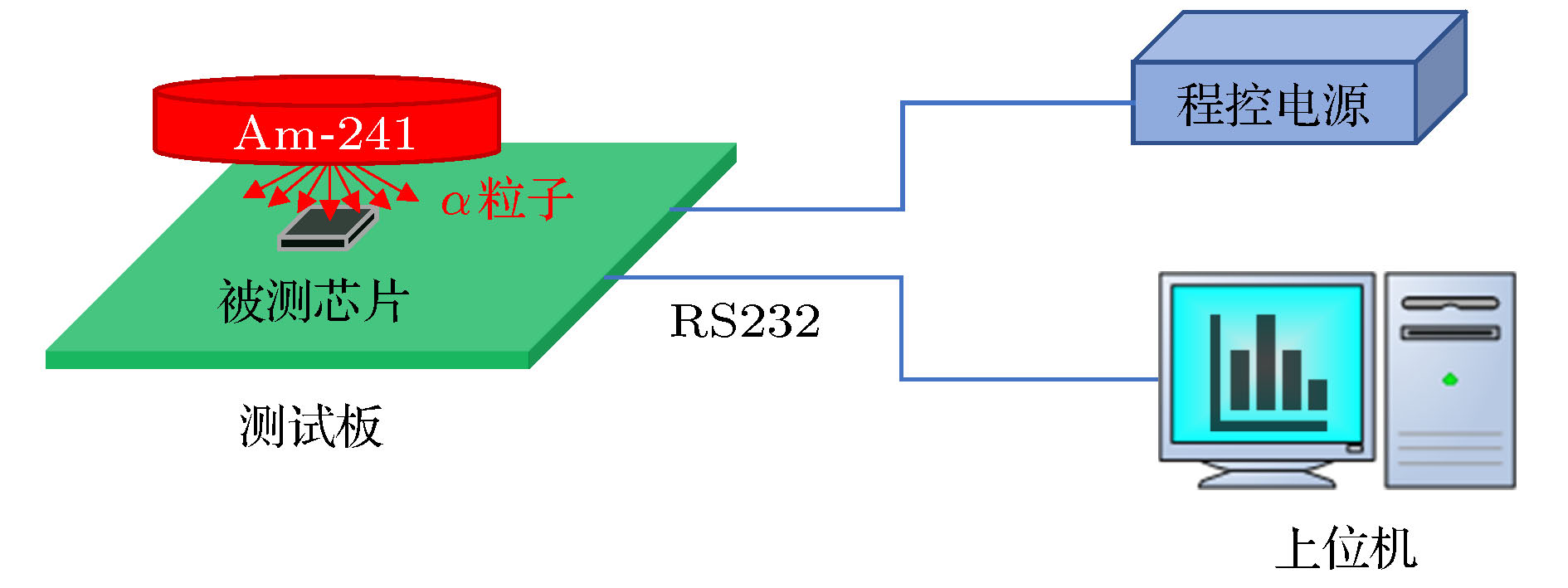
In this paper, the Am-241 is used as an alpha particle radioactive source to investigate the soft error mechanism in 65-nm and 90-nm static random accessmemory (SRAM). Combining reverse analysis, TRIM and CREME-MC Monte Carlo simulation, the energy transport process, deposited energy spectrum and cross-section characteristics of alpha particles in the device are revealed. The results show that the soft error sensitivity of the 65-nm device is much higher than that of the 90-nm device, and no flipping polarity is found. According to the real-time measured soft error rate at an altitude of 4300 m in Tibetan Yangbajing area, the thermal neutron sensitivity and alpha particle soft error rate, the overall soft error rate of 65-nm SRAM used at sea level of Beijing city is 429 FIT/Mb, and the contribution from alpha particles is 70.63%. Based on the results of reverse analysis, a three-dimensional simulation model of the device is constructed to study the influence of the incident angle of alpha particles on the single event upset characteristics. It is found that the corresponding deposition energy value at the peak of the number of particles in the sensitive region decreases by 40% with the incident angle increasing from 0° to 60°. While the single event upset cross sectionincreases by 79% due to the apparent single event upset edge effect in a sensitive region of the 65-nm device.
-
Keywords:
- alpha particle /
- soft error /
- single event upset /
- accelerated test
[1] May T C, Woods M H 1979 IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. ED-26 2
[2] Bhuva B 2018 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) San Francisco, CA, USA, December 1−5, 2018 p34.4.1
[3] Lei Z F, Zhang Z G, En Y F, Huang Y 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 066105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 王勋, 张凤祁, 陈伟, 郭晓强, 丁李利, 罗尹虹 2019 物理学报 68 052901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X, Zhang F Q, Chen W, Guo X Q, Ding L L, Luo Y H 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 052901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] JESD89 A Measurement and Reporting of Alpha Particle and Terrestrial Cosmic Ray-Induced Soft Errors in Semiconductor Devices JEDEC standard, October 2006 [标准]
[6] Auden E C, Quinn H M, Wender S A, O’ Donnell J M, Lisowski P W, George J S, Xu N, Black D A, Black J D 2020 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 67 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Weulersse C, Houssany S, Guibbaud N, Segura-Ruiz J, Beaucour J, Miller F, Mazurek M 2018 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 65 1851
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Autran J L, Munteanu D, Sauze S, Gasiot G, Roche P 2014 IEEE Radiation Effects Data Workshop (REDW) Paris, France, July 14−18, 2014 p1
[9] Lee S, Uemura T, Monga U, Choi J H, Kim G, Pae S 2017 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium (IRPS) Monterey, CA, USA, April 2−6, 2017 pSE-1.1
[10] Uemura T, Lee S, Min D, Moon I, Lim J, Lee S, Sagong H C, Pae S 2018 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium (IRPS) Burlingame, CA, USA, March 11−15, 2018 pSE.1-1
[11] Fang Y, Oates A S 2018 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium (IRPS) Burlingame, CA, USA, March 11−15, 2018 p4C.2-1
[12] Zhang Z, Lei Z, Tong T, Li X, Xi K, Peng C, Shi Q, He Y, Huang Y, En Y 2019 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 66 1368
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] The Stopping and Range of Ions in Matter, Ziegler J F http://www.srim.org/ [2019-7-3]
[14] Ziegler J F, Biersack J P, Littmark U 1985 The Stopping and Range of Ions in Solids (New York: Pergamon Press)
[15] Adams J H, Barghouty A F, Mendenhall M H, Reed R A, Sierawski B D, Warren K M, Watts J W, Weller R A 2012 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 59 3141
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Tylka A J, Adams J H, Boberg P R, Brownstein B, Dietrich W F, Flueckiger E O, Petersen E L, Shea M A, Smart D F, Smith E C 1997 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 44 2150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Weller R A, Mendenhall M H, Reed R A, Schrimpf R D, Warren K M, Sierawski B D, Massengill L W 2010 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 57 1726
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Mendenhall M H, Weller R A 2012 Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 667 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhang Z, Lei Z, En Y, Liu J 2016 Radiation Effects on Components & Systems Conference (RADECS) Bremen, Germany, September 19−23, 2016 PH14
[20] Gu S, Liu J, Zhao F Z, Zhang Z G, Bi J S, Geng C, Hou M D, Liu G, Liu T Q, Xi K 2015 Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 342 286
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 张战刚 2013 博士学位论文 (北京: 中国科学院大学)
Zhang Z G 2013 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
-
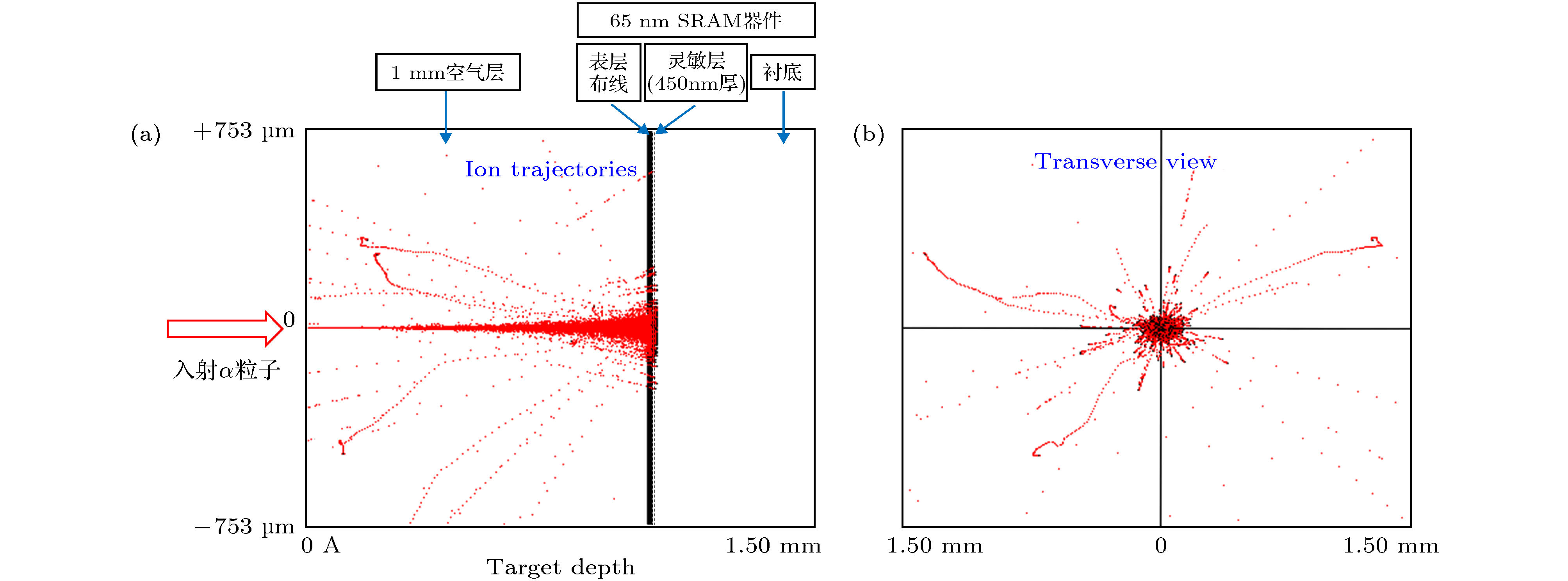
图 6 TRIM仿真结果 (a) α粒子在器件中的传播轨迹; (b)器件横断面视角下的α粒子轨迹(粒子初始入射位置为中心零点处)
Figure 6. TRIM simulation results: (a) The propagation trajectory of alpha particles in the device; (b) the alpha particle trajectory from the cross-sectional view of the device (the initial incident position of the particle is at the zero center).
表 1 使用的放射源参数
Table 1. Parameters of the radioactive source being used.
α粒子源 Am-241 放射率/粒子·2π–1·min–1 5.73 × 105 尺寸 圆柱体, Φ18 mm, 1 mm厚 表 2 被测器件参数
Table 2. Parameters of the devices under test.
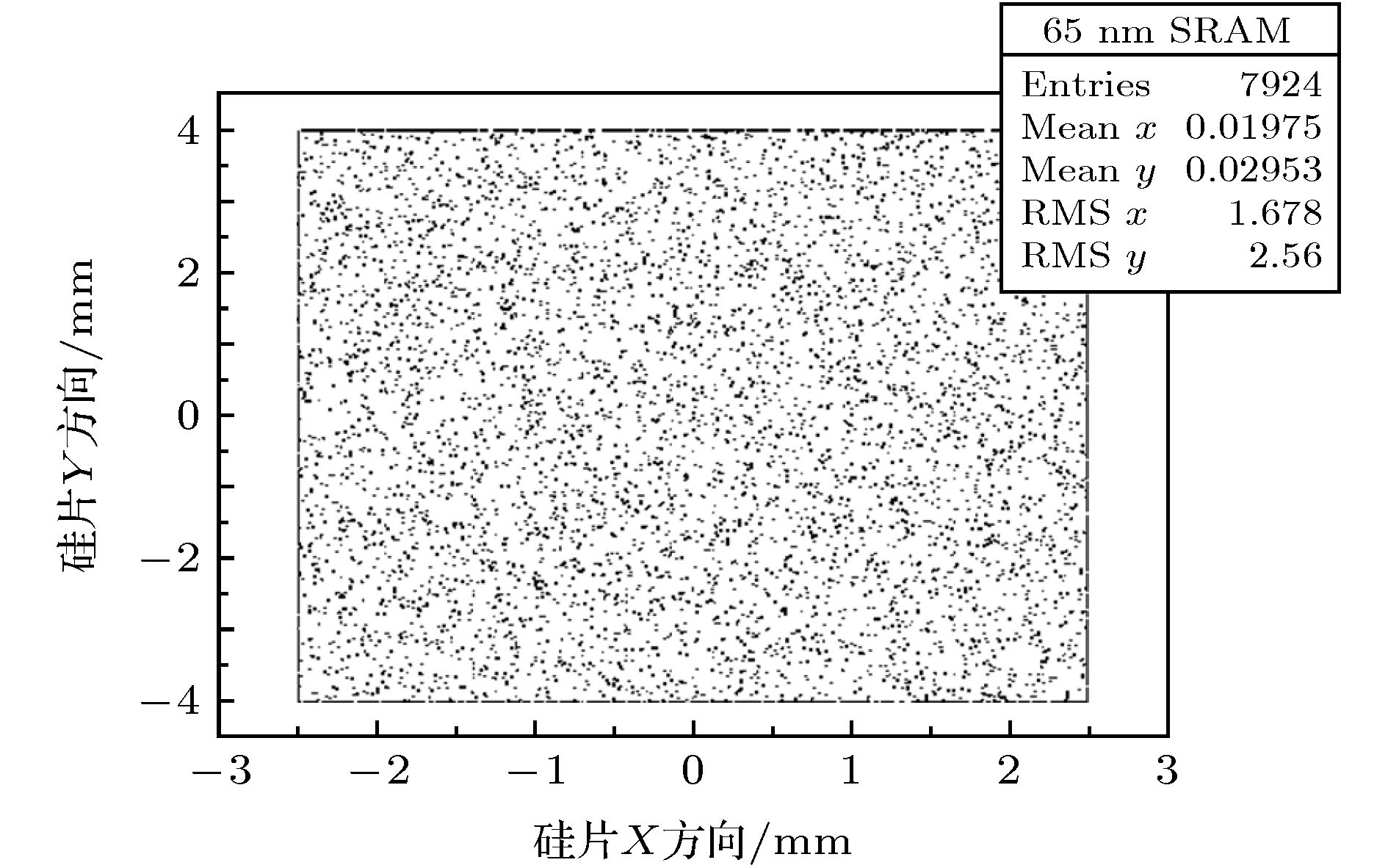
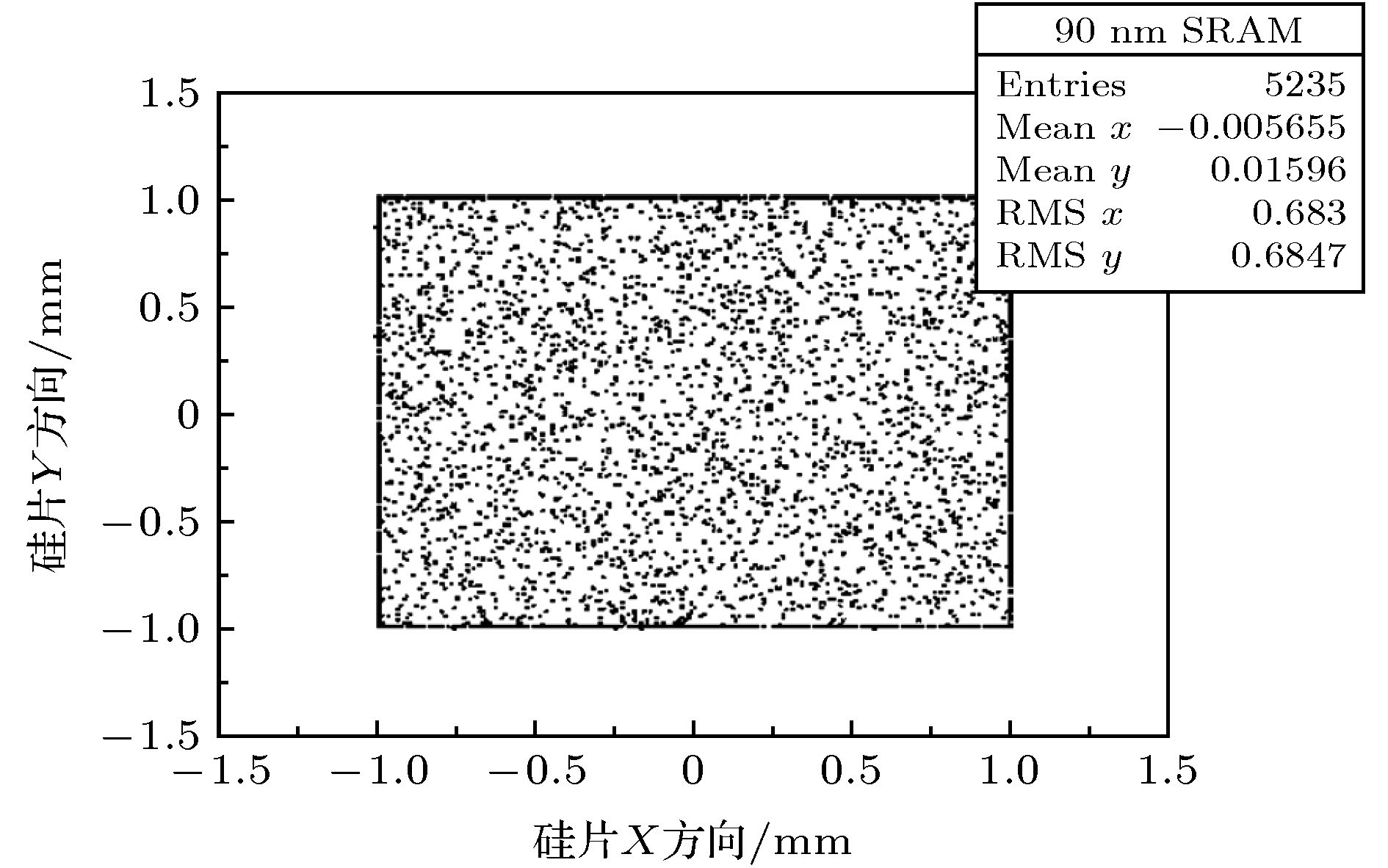
器件类型 型号 厂商 工艺尺寸/nm 测试容量/Mb 工作电压/V 硅片尺寸 DDR-II SRAM CY7C1318 CYPRESS 65 1.125 1.8 5 mm × 8 mm QDR-II SRAM CY7C1412 CYPRESS 65 18 1.8 5 mm × 8 mm SRAM CY7C1019D CYPRESS 90 1 3.3 2 mm × 2 mm 表 3 SEU截面测试结果
Table 3. Test results of SEU cross section.
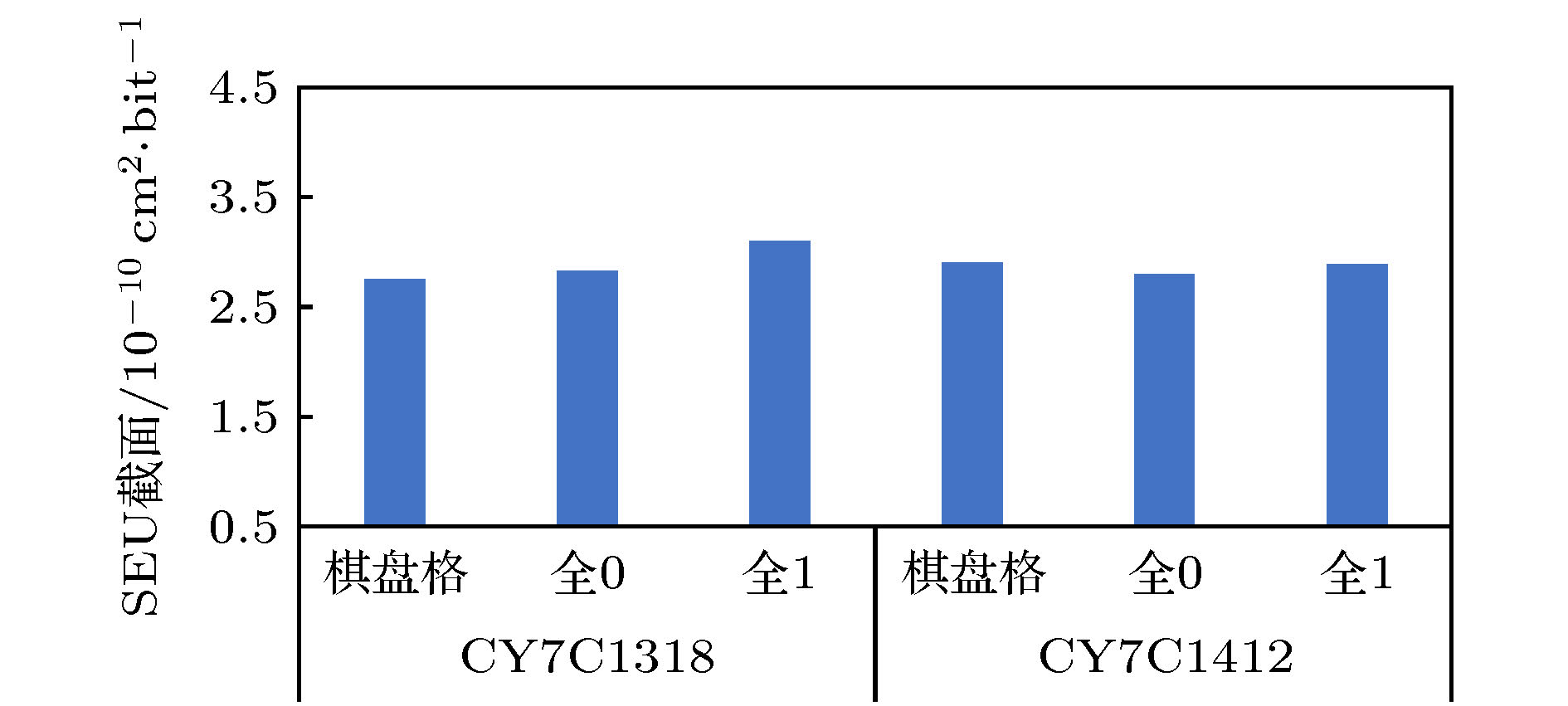
器件 测试容量/Mb 粒子注量率/cm–2·s–1 测试时长 SEU数量 SEU截面/cm2·bit–1 CY7 C1318(65 nm) 1.125 1.33 × 103 7 min 52 s 204 2.76 × 10–10 CY7 C1412(65 nm) 18 1.33 × 103 3 min 41 s 1613 2.91 × 10–10 CY7 C1019 D(90 nm) 1 7.42 × 102 16 h 127 2.83 × 10–12 表 4 α粒子发射率等级及对应的软错误率
Table 4. The α particle emissivity level and corresponding soft error rate.
α粒子发射率等级 发射率/cm–2·h–1 65 nm SRAM软错误率/FIT·Mb–1 90 nm SRAM软错误率/FIT·Mb–1 ULA ~0.001 3.03 × 102 2.97 Low Alpha (LA) ~0.01 3.03 × 103 29.7 Uncontrolled Alpha ~20 6.06 × 106 5.94 × 104 表 5 65 nm SRAM在4300 m海拔试验地点及北京海平面使用时的软错误率及α粒子、高能中子和热中子贡献占比
Table 5. Soft error rates of the 65 nm SRAM at the experimental site with an altitude of 4300 m and sea level of Beijing city being used. The contribution rates of α particle, high energy neutron and thermal neutron are analyzed, respectively.
粒子种类 4300 m海拔处的软错误率/FIT·Mb–1 占比(4300 m海拔) 北京海平面处的软错误率/FIT·Mb–1 占比(北京海平面) 全部 2356 100% 429 100% α粒子 303 12.86% 303 70.63% 高能中子 2053 87.14% 126 29.37% 热中子 0 0% 0 0% -
[1] May T C, Woods M H 1979 IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. ED-26 2
[2] Bhuva B 2018 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) San Francisco, CA, USA, December 1−5, 2018 p34.4.1
[3] Lei Z F, Zhang Z G, En Y F, Huang Y 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 066105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 王勋, 张凤祁, 陈伟, 郭晓强, 丁李利, 罗尹虹 2019 物理学报 68 052901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X, Zhang F Q, Chen W, Guo X Q, Ding L L, Luo Y H 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 052901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] JESD89 A Measurement and Reporting of Alpha Particle and Terrestrial Cosmic Ray-Induced Soft Errors in Semiconductor Devices JEDEC standard, October 2006 [标准]
[6] Auden E C, Quinn H M, Wender S A, O’ Donnell J M, Lisowski P W, George J S, Xu N, Black D A, Black J D 2020 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 67 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Weulersse C, Houssany S, Guibbaud N, Segura-Ruiz J, Beaucour J, Miller F, Mazurek M 2018 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 65 1851
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Autran J L, Munteanu D, Sauze S, Gasiot G, Roche P 2014 IEEE Radiation Effects Data Workshop (REDW) Paris, France, July 14−18, 2014 p1
[9] Lee S, Uemura T, Monga U, Choi J H, Kim G, Pae S 2017 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium (IRPS) Monterey, CA, USA, April 2−6, 2017 pSE-1.1
[10] Uemura T, Lee S, Min D, Moon I, Lim J, Lee S, Sagong H C, Pae S 2018 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium (IRPS) Burlingame, CA, USA, March 11−15, 2018 pSE.1-1
[11] Fang Y, Oates A S 2018 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium (IRPS) Burlingame, CA, USA, March 11−15, 2018 p4C.2-1
[12] Zhang Z, Lei Z, Tong T, Li X, Xi K, Peng C, Shi Q, He Y, Huang Y, En Y 2019 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 66 1368
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] The Stopping and Range of Ions in Matter, Ziegler J F http://www.srim.org/ [2019-7-3]
[14] Ziegler J F, Biersack J P, Littmark U 1985 The Stopping and Range of Ions in Solids (New York: Pergamon Press)
[15] Adams J H, Barghouty A F, Mendenhall M H, Reed R A, Sierawski B D, Warren K M, Watts J W, Weller R A 2012 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 59 3141
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Tylka A J, Adams J H, Boberg P R, Brownstein B, Dietrich W F, Flueckiger E O, Petersen E L, Shea M A, Smart D F, Smith E C 1997 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 44 2150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Weller R A, Mendenhall M H, Reed R A, Schrimpf R D, Warren K M, Sierawski B D, Massengill L W 2010 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 57 1726
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Mendenhall M H, Weller R A 2012 Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 667 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhang Z, Lei Z, En Y, Liu J 2016 Radiation Effects on Components & Systems Conference (RADECS) Bremen, Germany, September 19−23, 2016 PH14
[20] Gu S, Liu J, Zhao F Z, Zhang Z G, Bi J S, Geng C, Hou M D, Liu G, Liu T Q, Xi K 2015 Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 342 286
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 张战刚 2013 博士学位论文 (北京: 中国科学院大学)
Zhang Z G 2013 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 6498
- PDF Downloads: 72
- Cited By: 0













 DownLoad:
DownLoad: